

To determine EIRP follow this equation: - Cable Loss + Antenna Gain = EIRP. The last three things I will kind of explain is the EIRP, Free Space Path Loss, and Client side.ĮIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power) is the actual amount of signal leaving the antenna and is a value measured in db that is based on 3 things:Transmit Power (db), Cable Loss (db), & Antenna Gain (dbi). In general the Cisco APs have the following maximum transmit powers: 802.11a/n is 40mw or 14dbm, 802.11b is 100mw or 20dbm, 802.11g is 50mw or 17dbm although in some cases countries and specific channels can alter these limits. RSSI (Recieved Signal Strength Indicator) is a more common name for the Signal value meaning it is the strength that the device is hearing a specific device or signal.RSSI is most common used in bridge links where on client laptops they just call it Signal.Īs for your question about the maximum and minimum supported by cisco access points that is hard to answer because the antennas attached to the access points also factor into it. 55db + -95db = 40db this means you have an SNR of 40, my general rule of thumb is that any SNR above 20 is good. So to calculate your SNR value you add the Signal Value to the Noise Value and it generates (or should) a positive number that is expressed in decibels (db) for example lets say your Signal value is -55db and your Noise value is -95db. Typical environments range between -90db and -98db.
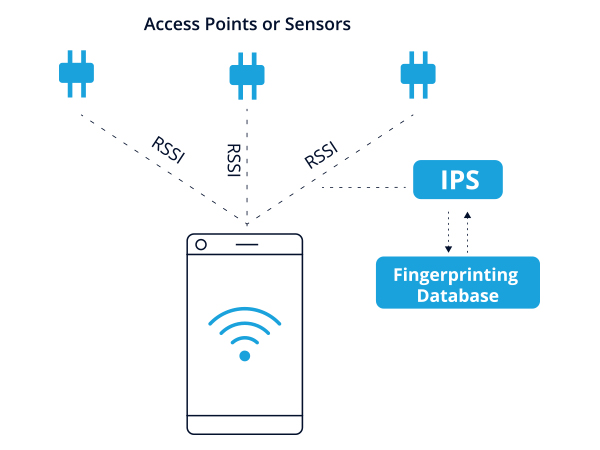
This value is measured in decibels from 0 (zero) to -120 (minus 120) now when looking at this value the closer to -120 (minus 120) is better because that means there is little to no interference. Now to the Noise side of this equation, noise is any signal (interference) that is not WiFi traffic such as cordless phones, microwaves, radar, etc. Normal range in a network would be -45db to -87db depending on power levels and design since the Signal is affected by the APs transmit power & antenna aswell as the clients antenna (I'll explain this later.) So we will look at the Signal (Also known as RSSI) first this value is measured in decibels from 0 (zero) to -120 (minus 120) now when looking at this value the closer to 0 (zero) the stronger the signal is which means it's better, typically voice networks require a -65db or better signal level while a data network needs -80db or better. SNR is comprised of 2 values and is measured as a positive value between 0db and 120db and the closer it is to 120db the better: Signal Value and Noise Value typically these are expressed in decibels (db). So let's look at the components of the SNR and they see how to determine it. SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) is a ratio based value that evaluates your signal based on the noise being seen. Values are how they relate to clients, and how they relate to connectivity. I am not really sure what you asking here, but My guess is your trying to get a grasp on what SNR and RSSI


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
